Calculators
powertechno2024-01-29T11:08:35-06:00Calculators
Fan Angle Calculator
To achieve your desired projection, select a minimum fan angle of: degrees | ||||
|
Meters Centimeters Feet Inches | 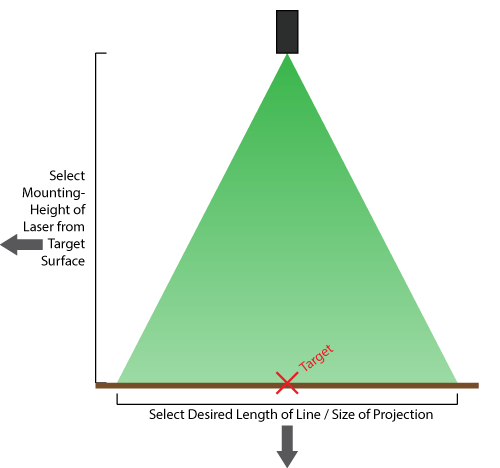 |
|||
| Meters Centimeters Feet Inches | ||||
Divergence Calculation
| Distance [m]: | |
| Laser: | |
| Power [mW]: | |
| Divergence [mrad]: | |
| Diameter at aperture [mm]: | |
| Beam diameter after m: | mm |
| Area of laser point after m: | mm2 |
| Laser intensity of uniform beam after m: | mW/mm2 |
Find a laser beam's divergence
| Specifications: | |
| Distance from Laser Aperture -> Projection surface [m]: | |
| Beam Waist Diameter at Laser Aperture [mm]: | |
| Laser spot diameter at the projection surface [mm]: | |
| The Full Divergence of the laser system is: |
| 0.00 mrad |
Calculating nanometers from wavenumber
Converting angstroms to nanometers
To convert from angstroms to nanometers, use the following equation:
1 angstrom = 0.1 nanometer. Or use the tool below.
Converting fahrenheit to celsius
To convert from fahrenheit to celsius, use the following equation:
32° Fahrenheit = 0° Celsius. Or use the tool below.
Converting watts to joules
Power is measured in Watts, named after James Watt (1736-1819). Joules (named after James Prescott Joule, 1818-1889) are units of energy. Use the following equation to convert from Watts to Joules.
1 Watt = 1 Joule per second of power
Calculating duty factor
Duty factor (also known as duty cycle) is the ratio of pulse duration to pulse period. Duty factor (Df) is calculated as follows.
Df = pulse duration (sec) / pulse repetition period (sec)
Multiply the result by 100 to get your answer as a percentage.
Please note that as pulse repetition frequency increases, duty factor increases. As pulse repetition period increases, duty factor decreases. As pulse duration increases, duty factor increases.
Converting wavelength to frequency
You can use the following equation to convert wavelength to frequency:
v (Hz) = 2.998 x 1017 / wavelength (nm).
Contact Us
For custom quotes and more information about our laser technology services, please call, chat or submit our online form below.
